The Future of Blind Spot Monitoring: Technology Advancements
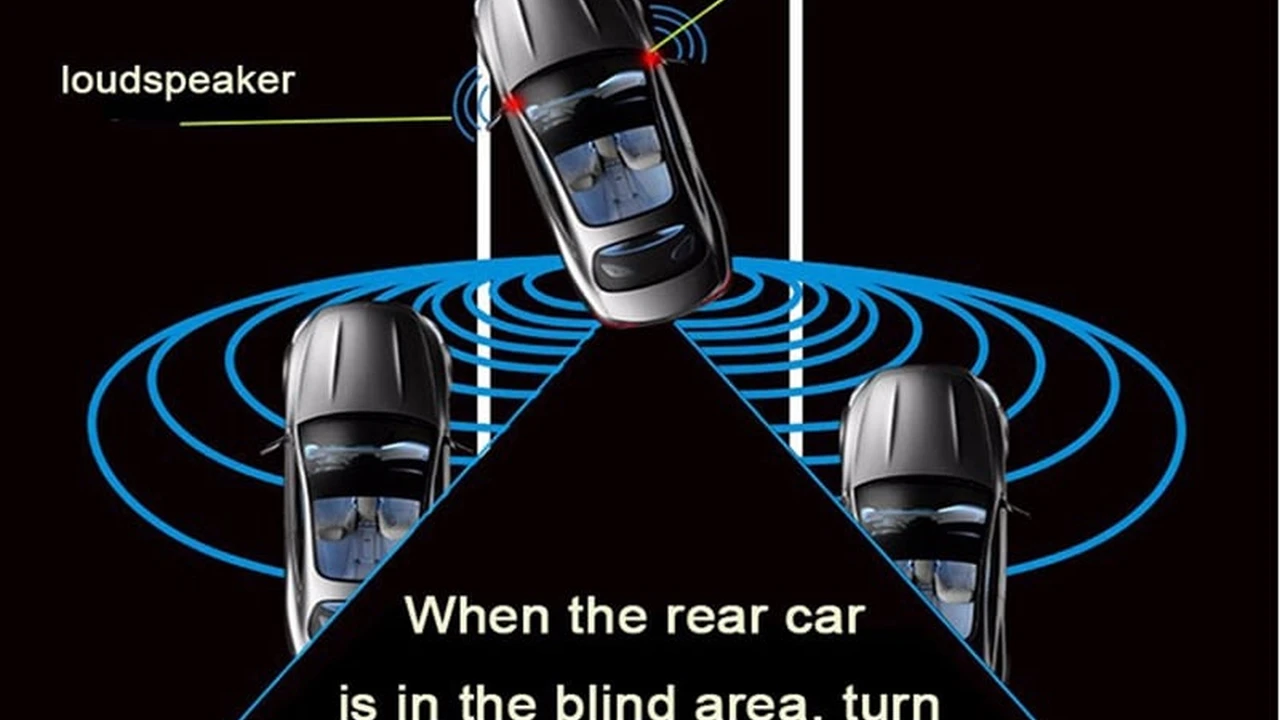
Introduction to Blind Spot Monitoring Systems
Alright, let's talk about blind spot monitoring, or BSM as the cool kids call it. You know, those pesky areas you can't quite see when you're changing lanes? Yeah, BSM is designed to be your extra set of eyes, a digital wingman ensuring you don't accidentally merge into another car. It's come a long way from the early days, and frankly, it's pretty darn impressive now. We're not just talking about a simple light in the mirror anymore; it's a whole ecosystem of sensors and algorithms working together.
The Evolution of Blind Spot Detection Technology
Where did this all start? Well, early systems were pretty basic, relying on radar sensors to detect vehicles in your blind spots. These systems would trigger a visual or audible alert – usually a light on the side mirror or a beep – to warn you. The problem was, they weren't always accurate and could be prone to false alarms. Think about driving past a guardrail or a stationary object – those early systems might freak out. Over time, the technology improved significantly. We moved from simple radar to more sophisticated radar and even camera-based systems. These newer systems are much better at distinguishing between actual vehicles and stationary objects, reducing those annoying false alarms. They're also more accurate at detecting vehicles at different speeds and in different weather conditions.
How Blind Spot Monitoring Works Today: Sensors and Algorithms
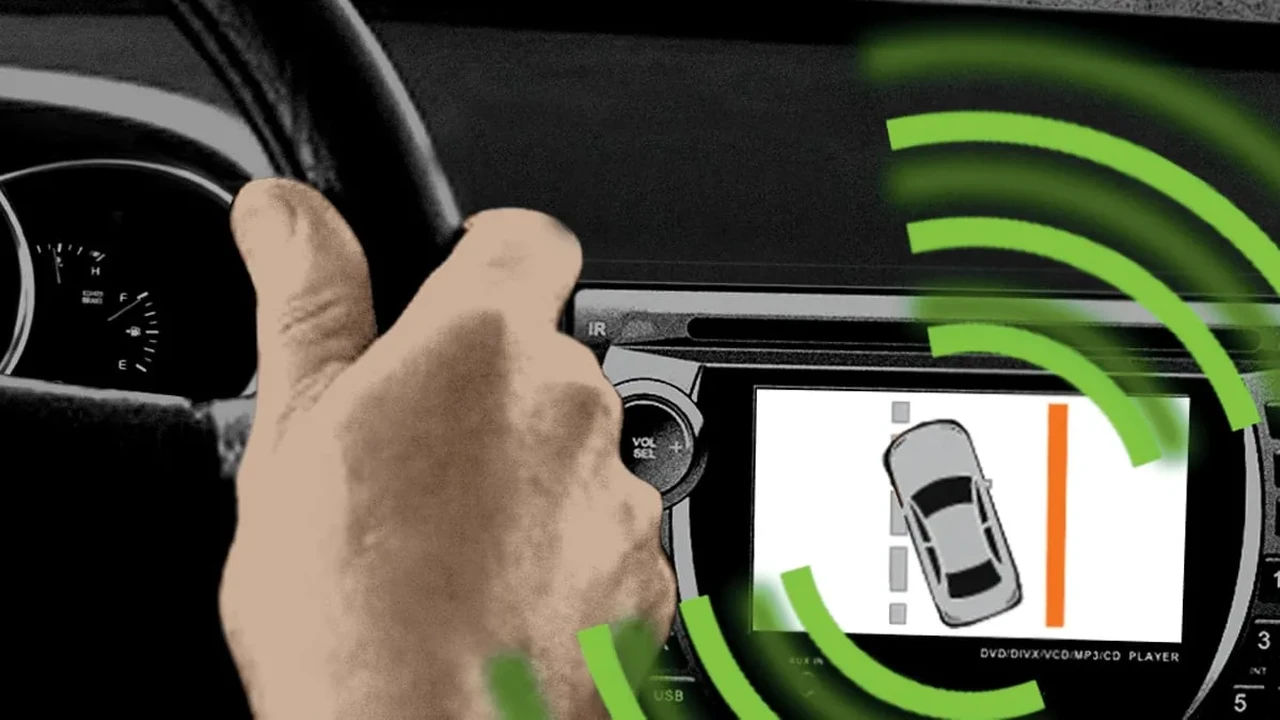
So, how does BSM work in 2024? It's a combination of hardware and software magic. Most systems use radar sensors, typically mounted in the rear bumper, to scan the areas beside and behind the vehicle. Some systems also incorporate cameras, often mounted in the side mirrors, to provide a visual confirmation of what's in the blind spot. The data from these sensors is fed into a central processing unit (ECU) that uses sophisticated algorithms to analyze the information and determine if a vehicle is present in the blind spot. These algorithms take into account factors like speed, distance, and direction to provide an accurate assessment of the situation. If the system detects a vehicle and you activate your turn signal to merge into that lane, it will trigger an alert – usually a visual warning in the side mirror, an audible beep, or even a steering wheel vibration – to warn you of the potential danger.
Advancements in Blind Spot Monitoring Systems: Beyond Simple Detection
BSM isn't just about detecting vehicles anymore; it's about preventing accidents. Modern systems are incorporating a range of advanced features to enhance safety. For example, some systems now include lane change assist, which actively helps you steer the vehicle back into your lane if you start to drift while a vehicle is in your blind spot. Others include rear cross-traffic alert, which warns you of approaching vehicles when you're backing out of a parking space. And some even integrate with the vehicle's adaptive cruise control system to automatically adjust your speed to maintain a safe distance from vehicles in your blind spots. The integration with other safety systems is really the key here. BSM is becoming part of a larger safety net, working in conjunction with other technologies to provide a comprehensive safety solution.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Enhancing Blind Spot Monitoring Accuracy and Reliability
AI and machine learning are revolutionizing BSM. These technologies are being used to improve the accuracy and reliability of BSM systems by allowing them to learn from data and adapt to changing conditions. For example, AI algorithms can be trained to recognize different types of vehicles, such as motorcycles and bicycles, which can be difficult for traditional radar-based systems to detect. They can also learn to identify patterns and predict potential hazards, such as a vehicle that is rapidly approaching from behind. Machine learning is also being used to improve the accuracy of BSM systems in challenging weather conditions, such as rain, snow, and fog. By analyzing data from sensors and cameras, AI algorithms can compensate for the effects of weather and provide a more reliable assessment of the situation. The more data these systems collect, the smarter they get, leading to fewer false alarms and more accurate warnings.
Specific Blind Spot Monitoring Products: Features, Use Cases, Comparisons, and Pricing
Okay, let's get down to brass tacks and talk about some specific products. Here are a few options, covering a range of features and price points:
H2 Aftermarket Blind Spot Monitoring Systems: Cost-Effective Blind Spot Monitoring Solutions
If your car doesn't have BSM from the factory, don't despair! There are plenty of aftermarket options available. These systems typically involve installing radar sensors in the rear bumper and connecting them to a control unit and visual alerts (usually LEDs that stick onto your side mirrors).
Brand A: Brand A Blind Spot Monitoring System - Comprehensive Coverage
Features: This system uses dual radar sensors for wide-angle coverage, adjustable sensitivity, and audible alerts. It's compatible with most vehicles and relatively easy to install (though professional installation is recommended). Use Cases: Ideal for older vehicles or those with basic safety features. It provides a significant upgrade in safety and peace of mind. Comparison: Offers wider coverage than some cheaper alternatives but may not be as accurate in heavy traffic. Price: Around $200 - $300.
Brand B: Brand B Blind Spot Monitoring System - Budget-Friendly Option
Features: A more basic system with single radar sensor and visual alerts. It's a simple and affordable way to add BSM to your vehicle. Use Cases: A good option for drivers who primarily want basic blind spot detection without advanced features. Comparison: Less accurate and less comprehensive than Brand A, but significantly cheaper. Price: Around $100 - $150.
H2 OEM Integrated Blind Spot Monitoring Systems: Advanced Features and Seamless Integration
These are the systems that come standard on many new cars. They're typically more sophisticated and integrated with the vehicle's other safety systems.
Car Model X: Car Model X Blind Spot Monitoring System - Lane Keep Assist Integration
Features: This system uses radar and camera-based sensors, lane keep assist integration (automatically steers you back into your lane if you drift), and rear cross-traffic alert. Use Cases: Designed for drivers who want the highest level of safety and convenience. The lane keep assist feature is particularly helpful on long highway drives. Comparison: More expensive than aftermarket options but offers superior performance and integration. Price: Included as part of an option package, typically costing $2,000 - $3,000.
Car Model Y: Car Model Y Blind Spot Monitoring System - Simplified Alerts
Features: Radar-based system with visual and audible alerts. It's designed to be less intrusive than some other systems, with more subtle alerts. Use Cases: Ideal for drivers who find some BSM systems to be too distracting. The simplified alerts are less likely to cause driver fatigue. Comparison: May not be as noticeable as other systems in certain situations. Price: Included as a standard feature or as part of a relatively inexpensive option package.
H2 Considerations When Choosing a Blind Spot Monitoring System: Factors Affecting Performance and Suitability
Choosing the right BSM system depends on your needs and budget. Here are a few things to consider:
- Accuracy: How accurately does the system detect vehicles in your blind spots?
- False Alarms: How often does the system trigger false alarms?
- Coverage: How wide is the coverage area?
- Features: What additional features are included, such as lane change assist or rear cross-traffic alert?
- Integration: How well does the system integrate with the vehicle's other safety systems?
- Price: How much does the system cost?
- Installation: How easy is the system to install? (Aftermarket systems)
The Future of Blind Spot Monitoring: What's Next?
The future of BSM is bright! We can expect to see even more advanced features, such as:
- 3D Mapping: Using 3D maps to provide a more accurate representation of the surrounding environment.
- V2X Communication: Communicating with other vehicles and infrastructure to provide even earlier warnings of potential hazards.
- Enhanced Sensor Fusion: Combining data from multiple sensors to provide a more comprehensive view of the surrounding environment.
- Predictive Algorithms: Using AI to predict potential hazards before they occur.
Ultimately, BSM is about making driving safer and more comfortable. As the technology continues to evolve, it will play an increasingly important role in preventing accidents and saving lives.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/277019-baked-pork-chops-with-cream-of-mushroom-soup-DDMFS-beauty-4x3-BG-7505-5762b731cf30447d9cbbbbbf387beafa.jpg)






